Remarkable developments in additive manufacturing technologies over the past few decades have transformed the potential ways in which products are designed, developed, manufactured, fabricated, and distributed.
In What Areas 3D Printing is Especially Good
Shifting from conventional production processes to 3D printing technologies have revolutionised companies from various industries in improving the technical and business aspects of parts and products but there are two major areas where AM will have greatest influence pertaining to the automotive sector.
Product Innovation
Additive Manufacturing can produce components with fewer design restrictions that are tough to produce using traditional manufacturing processes. This design flexibility paves a way for innovation by making it possible to add improved functionalities such as integrated electrical wiring (through hollow structures), lower weight (through lattice structures), and complex geometries that are not possible through traditional processes. Furthermore, new AM technologies are increasingly able to produce multi material printed parts with individual properties such as electrical conductivity and variable strength. These AM processes play an important role in creating safer, lighter, faster and more efficient vehicles of the future. EDAG’s Light Cocoon is a classic example of how AM can potentially open new doors in terms of innovation.
Supply Chain
AM cuts down on overall lead time by eliminating the need for new tooling and directly producing final parts. In addition, since AM generally uses only the material that is necessary to produce a component, using it can drastically reduce scrap and drive down material usage. Furthermore, AM-manufactured lightweight components can lower handling costs, while on-demand and on-location production can lower inventory costs, providing a flexible supply chain. Finally, AM can support decentralized production at low to medium volumes including cost reductions and the improved ability to manufacture products closer to customers, reducing supply chain complexity.
Product Stages Where AM Can Be Applied
With its unique advantages, AM is capable of replacing a few processes that are conventionally used in automotive production. Here are four significant changes that AM can bring to the automotive industry.
Prototyping Process
Prototyping is normally time-consuming and ends up being expensive as a product goes through more iterations. Rapid prototyping (3D printing) enables companies to turn rough ideas into convincing validation of concept. These concepts can then further proceed to highly accurate prototypes that closely match the end result and ultimately guide products through a series of iterations and validation stages toward mass production. In the automotive industry, this rapid validation is of utmost importance. With 3D printing, highly convincing and representative prototypes can be created within a couple of days, at a much lower cost and shorten the distance between idea and final product, strengthening their overall product development workflows.
Repair and Support (Spare Parts)
With the help of CAD, designs for literally all parts can be stored as a digital copy in a computer hard drive, eliminating the need to maintain an inventory. With the use of 3D printing, a spare part could potentially be produced on-demand. The accessibility of the technology will encourage suppliers to open up new spaces to provide an easy supply of 3D printed components and spare parts. Even parts that no longer exist can potentially be remade to requirement, on reverse engineered based on digital scans of existing parts. Older designs may find themselves with a new lease of life and on the other side, spare parts of classic cars can be reproduced easily.
Customisation
Customising is highly expensive and time-intensive with conventional manufacturing processes. 3D printing is ideal for producing low-cost customized parts, providing manufacturers with new capabilities in what they are able to produce and offer to their customers. For smaller custom car shops – 3D printing car parts has provided ways of pushing the quality and creativity of their work, providing a lot of scope to experiments and perfect custom designs.
Serial Manufacturing (Assemblies of Various Parts)
3D printing can improve efficiency at the general parts manufacturing stage. You might have an assembly of five or six automotive parts that can now be combined in a single printed part. You’re saving assembly time and cost even if the individual part might be more expensive. By consolidating parts, 3D printing processes can also help decrease weight and improve fuel efficiency. It will make more sense from a productive l point of view to incorporate 3D printing further into general parts manufacture.
What Technologies and Materials Are Suitable
Ranging from plastic trims to metal engine components, AM has been proving itself and has more to offer in terms of the technology processes and the materials that can be used. This table gives a brief overview of the popular options.
| Application | Process | Material | Features | Examples |
| Interior and Seating | SLA, SLS, MJF | Polymers | Customized cosmetic components | Dashboards , Seat frames |
| Tires, wheels, suspension | SLS, MJF, DMLS | AluminIum Alloys, Polymers | Tough, sturdy components | Suspension springs, hubcaps |
| Electronics | SLS, MJF | Polymers | Delicate components | Sensors, Single part control panels |
| Exhausts and emissions | DMLS | Aluminium alloys | Hollow metal parts | Cooling vents |
| Under the hood | SLS, MJF | Nylon | Heat resisting functional part | Battery cover |
| Lights | SLA, MJF | Resin | Fully transparent, High detail | Headlights, Headlight prototypes |
| Airducts | SLS, MJF | Nylon | Flexible ducting | HVAC ducting |
| Prototypes | SLA | Polymers | High definition, clear details | Final high definition prototypes |
| Functional mounting brackets | SLS, SLM, MJF | Nylon PA12, titanium | Light weight, high strength | Alternator bracket |
| Complex engine parts | DMLS | Aluminium alloys | Consolidated, lightweight, functional metal parts | Wishbone suspension |
Current Industrial Use Examples
Many Automobile OEMS have already started to work with AM, realizing its capability and efficiency, here are 2 such examples
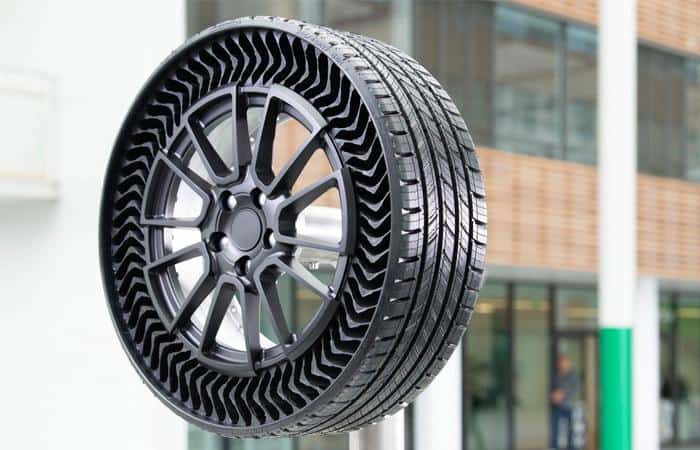
The 3D Printed Uptis Tires by Michelin
The French tire manufacturer, Michelin, presented its first prototype tire supported by additive manufacturing technologies in 2019. Called Uptis (Unique Puncture-proof Tire System), these tires have been designed to be airless in order to reduce the risk of flat tires and other air loss failures that result from puncture or road hazards. The design is only possible because of AM. If successful, we could expect Uptis to equip some cars by 2024. Finally, these puncture-proof tires can also decrease waste to promote sustainable mobility (one of the goals of the company’s future of mobility vision).

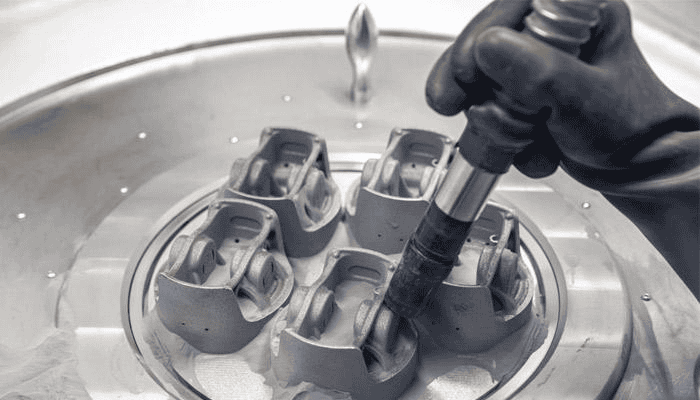
Porsche and the First 3D Printed Engine Pistons
The automotive giant Porsche 3D printed engine pistons for the first time ever. The additively manufactured components were designed for the high-performance engine of the Porsche 911 GT2. 3D printing allowed optimizing the pistons, and as a result, making this critical engine element 10% lighter than the traditionally manufactured ones. Porsche used a special aluminium alloy for the pistons in order to obtain the best properties for this specific application.

Conclusion
Considering the range of capabilities unlocked by AM, leaders of automotive companies should consider taking advantage of AM technologies to stay ahead of competition. While traditional manufacturing techniques are deeply rooted and will continue to hold a strong position in the automotive industry, additive manufacturing is making inroads.
Xometry works with top automotive manufacturers such as BMW, Tier 1 and 2 suppliers, and 44% of the Fortune 500 motor vehicles and parts companies to simplify their supply chain and dynamically scale their manufacturing capacity. Check out our 3D printing services!
 Europe
Europe  Türkiye
Türkiye  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Global
Global 

 Login with my Xometry account
Login with my Xometry account  0
0



 Download
Download